Syndromes/Craniofacial Anomalies
430 - Dental Abnormalities Related to Roifman Syndrome: A Case Report

ezza M. abdullah, DDS (she/her/hers)
student
University of Alabama at Birmingham
university of Alabama at Birmingham
Hoover, Alabama, United States
ezza M. abdullah, DDS (she/her/hers)
student
University of Alabama at Birmingham
university of Alabama at Birmingham
Hoover, Alabama, United States- JJ
Janice G. Jackson, DMD
Professor & Chair Department of Pediatric Dentistry
University of Alabama at Birmingham
birmingham, Alabama, United States 
Yu-Yin Lin, D.D.S.
Assistant Professor | Director, Pre-Doctoral Program in Pediatric Dentistry
University of Alabama at Birmingham
University of Alabama at Birmingham
Birmingham, Alabama, United States- PZ
Ping Zhang, D.D.S., Ph.D.
Professor and Director of Research
University of Alabama at Birmingham
University of Alabama at Birmingham
birmingham, Alabama, United States - PZ
Ping Zhang, D.D.S., Ph.D.
Professor and Director of Research
University of Alabama at Birmingham
University of Alabama at Birmingham
birmingham, Alabama, United States - JJ
Janice G. Jackson, DMD
Professor & Chair Department of Pediatric Dentistry
University of Alabama at Birmingham
birmingham, Alabama, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Research Mentor(s)
Program Director(s)
Introduction: Roifman syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by antibody deficiency, spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia, facial dysmorphism, growth retardation, and retinal dystrophy. Fewer than twenty patients with Roifman syndrome have been reported to date.
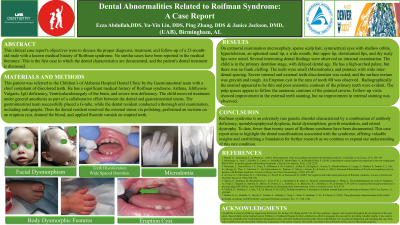
Case Report: This report details the diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of a 23-month-old male with a medical history of Roifman syndrome, asthma, ichthyosis vulgaris, IgG deficiency, ventricularulomegaly, and severe iron deficiency. To our knowledge, no similar cases have been documented, and this is the first case to describe the patient’s dental characteristics and treatment. The child was referred to the Children’s of Alabama Hospital Dental Clinic with a chief complaint of discolored teeth. The patient was examined and treated under general anesthesia. Extraoral examination revealed microcephaly, sparse scalp hair, symmetrical eyes with shallow orbits, hypertelorism, an upturned nasal tip, a wide mouth, a thin upper lip, downturned lips, and dry, scaly lips. Intraoral examination showed that the child was in the primary dentition stage with delayed dental age, a high-arched palate (without clefting), small (microdontia) and pointed teeth with wide inter-dental spacing, and severe internal and external discoloration with grayish, rough texture. An eruption cyst was noted in the area of tooth #B. Radiographs revealed thin enamel, poor anatomic contours, and enlarged pulp spaces (taurodontism). External stains were removed through polishing, and the eruption cyst was incised and drained. Follow-up visits showed improvement in external staining, but no change in internal staining was observed.
Identify Supporting Agency and Grant Number:

.jpg)