Oral Pathology
303 - Soft Tissue Excisional Biopsy of a Recurrent Lower Lip Mucocele in a 7 Year Old Male

Robert R. Bauer, DMD
PGY-2
Children’s Hospital of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI
Children's Hospital of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI
Cape Girardeau, MO, Missouri, United States- CG
Colleen C. Greene, DMD
Section Chief
Children’s Hospital of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI
Milwaukee, Wisconsin, United States - CD
Carli DiGioia, DMD
Program Director
Children’s Hospital of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI
Milwaukee, Wisconsin, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Research Mentor(s)
Program Director(s)
Purpose:
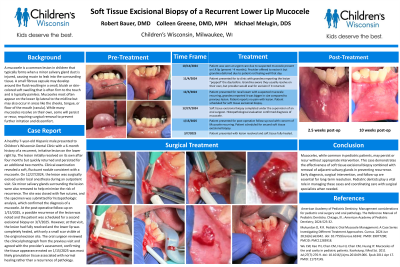
To describe the clinical presentation, surgical management, and outcomes of a recurrent mucocele located on the lower lip of a pediatric patient.
Methods:
A 7-year-old male presented to Children's Wisconsin Dental Clinic with a recurrent, irritative lesion on the lower right lip, persisting for 3 months. Clinical examination revealed a soft, fluctuant nodule consistent with a mucocele. The lesion initially resolved on its own after one month but then returned a few days later and persisted for two months. Under the guidance of an oral surgeon, the lesion was excised in an outpatient visit under local anesthesia via a soft tissue biopsy, which included removal of six minor salivary glands in the surrounding tissue to reduce recurrence risk. Five sutures were placed to close the excision site. The specimen was submitted for histopathological analysis.
Results:
Pathology report confirmed the diagnosis of a mucocele. The biopsy was completed on 12/27/2024. Provider followed up with the patient’s mother one week after the procedure. Mother reported the patient is recovering well and has experienced no complications. The patient is scheduled to return for a follow-up evaluation on 1/15/2025.
Conclusions:
Soft tissue excisional biopsy with the concurrent removal of minor salivary glands is an effective treatment for lower lip mucoceles in pediatric patients. This case highlights the importance of surgical precision and histopathological confirmation in achieving symptom resolution and preventing recurrence.
Identify Supporting Agency and Grant Number:

.jpg)