Trauma
Evaluating Evidence-Based Education for Caregivers of Children with Dental Trauma
51 - Evidence-Based Education for Caregivers of Children with Dental Trauma

Mikaela Lujan, DDS (she/her/hers)
Pediatric Dental Resident
The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
The Ohio State University and Nationwide Children's Hospital
columbus, Ohio, United States- JT
Janice Townsend, DDS, MS
Nationwide Childrens Hospital

Daniel Claman, DDS
Chief of Dentistry
Nationwide Children's Hospital
The Ohio State University/Nationwide Children's Hospital
Columbus, Ohio, United States
David O. Danesh, DMD, MPH, MS (he/him/his)
Adjunct Assistant Professor
The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio
The Ohio State University, College of Dentistry
Columbus, Ohio, United States- JP
Jin Peng, MD, MS, PhD
Nationwide Children's Hospital
- JM
Jodee McDaniel, BSDH, EFDA, MS
Nationwide Children's Hospital

Ehsan N. Azadani, DDS, MS
Assistant Professor and Attending
The Ohio State University and Nationwide Children's Hospital
The Ohio State University and Nationwide Children's Hospital
Columbus, Ohio, United States
Ehsan N. Azadani, DDS, MS
Assistant Professor and Attending
The Ohio State University and Nationwide Children's Hospital
The Ohio State University and Nationwide Children's Hospital
Columbus, Ohio, United States
Kim Hammersmith, DDS, MPH, MS
Program Director
The Ohio State University and Nationwide Children's Hospital
The Ohio State University and Nationwide Children's Hospital
Columbus, Ohio, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Research Mentor(s)
Program Director(s)
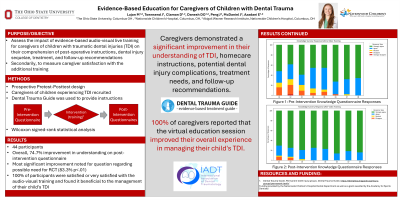
Purpose: To evaluate the impact of individualized evidence-based education of traumatic dental injuries (TDI) on caregivers’ understanding and measure their satisfaction with the experience.
Methods: Caregivers of children experiencing a TDI in the permanent dentition were recruited. The caregiver’s knowledge regarding the child’s TDI was assessed via an eight question Likert style survey given before and after presentation of individually tailored audio-visual education. A separate eight question Likert-style survey was completed to assess caregivers’ satisfaction with the education.
Results: 44 caregivers completed all aspects of this study. Overall, most caregivers, 74.7% eligible for improvement, showed an increase in their understanding regarding their child’s TDI. Caregivers overall reported high levels of satisfaction with 100% reporting stating Satisfied or Very Satisfied, and 100% reporting Strongly Agree or Agree to improvement in their understanding of their child’s TDI. All participants reported they felt more prepared for their child’s next dental visit. Caregivers struggled the most to identify the importance of helping their child with oral hygiene following dental injury.
Conclusions: Evidence-based audio-visual education increased caregiver knowledge of their child’s traumatic dental injuries. All participants expressed satisfaction with the training and found it beneficial in managing their child’s TDI.
Identify Supporting Agency and Grant Number: Research supported by Nationwide Children's Hospital departmental funds and the Academy for Sports Dentistry internal grant #SRA00000055

.jpg)