Oral Pathology
134 - Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) and Course-of-Care for Odontogenic Facial Swellings

Cassidy Boudreau, DMD
Dental Resident
Cincinnati Children’s Medical Center Hospital, Cincinnati, OH
Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center
Louisville, Kentucky, United States- ST
Sarat Thikkrissy, DDS, MS, MA
Cincinnati Children’s Medical Center Hospital, Cincinnati, OH

Patrick T. Ruck, DDS (he/him/his)
Assitant Professor
Cincinnati Children’s Medical Center Hospital, Cincinnati, OH
Cincinnati, Ohio, United States
Scott Schwartz, DDS, MPH
Associate Professor
Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center
Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center
Cincinnati, Ohio, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Research Mentor(s)
Program Director(s)
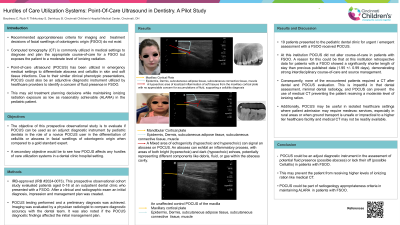
Purpose: Validated radiographic diagnostic criteria and corresponding treatment decisions for a facial swelling of odontogenic origin (FSOO) do not currently exist. Computed tomography (CT) is utilized in medical settings to assess facial swellings, but this is concerning due to the level of ionizing radiation used for CT. Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) has been utilized in medical settings to differentiate abscess and cellulitis in skin and soft tissue infections. Due to similar clinical phenotypic presentations, POCUS could also be an adjunctive diagnostic instrument utilized by healthcare providers to identify a concern of fluid presence in FSOO.
Methods: This IRB approved prospective observational cohort study evaluated patients aged 0-18 at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center outpatient dental clinic with a FSOO. After a clinical and intraoral radiographic exam, an initial diagnosis, and management plan was created. POCUS testing was then performed in a sagittal and transverse plane and a preliminary diagnosis was achieved. Imaging was evaluated by a physician radiologist to compare diagnostic accuracy with the dental team. It was also noted if the POCUS diagnostic findings affected the initial management plan.
Results: Preliminary data were collected from 18 subjects (7 male, 11 female) with a mean age of 9.3±5 years. Sixty percent of patients presented with erythema, 20% with induration, 94% with warmth to touch, 77% with fluctuance and vestibular obliteration. 47% presented with fluid collection present. 38% of patients were diagnosed with an abscess using the POCUS, while 61% were diagnosed with a cellulitis.
Conclusion: Final data pending.
Identify Supporting Agency and Grant Number:
Research Supported by CCHMC Technion Bridge to NextGen Grant $50,000

.jpg)