Preventive
69 - Comparing Acidity and Dental-hypersensitivity between Arginine Mouthrinse and SDF

Michael Mears, DMD (he/him/his)
Resident
Jamaica Hospital Medical Center
JHMC
Modesto, California, United States- LK
Luke Keating, Biostatistician
Jamaica Hospital Medical Center
Jamaica, New York, United States - LK
Luke Keating, Biostatistician
Jamaica Hospital Medical Center
Jamaica, New York, United States - JW
Jeannine L. Weiss, Board Certified Pediatric Dentist (American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry)
program director and clinical faculty
Jamaica Hospital Medical Center, Department of Dental Medicine, Division of Pediatric Dentistry
Jamaica, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Research Mentor(s)
Program Director(s)
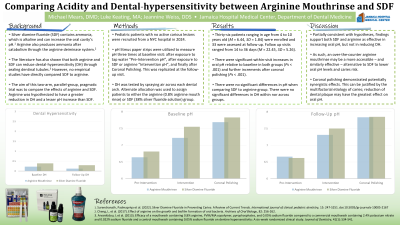
Purpose: Both arginine and silver diamine fluoride (SDF) can reduce dental-hypersensitivity (DH) and increase oral pH. However, no empirical studies have directly compared SDF to arginine. The aim of this two-arm, parallel-group, pragmatic trial was to compare effects of arginine and SDF. Arginine was hypothesized to have a greater reduction in DH and a lesser pH increase than SDF.
Methods: Pediatric patients with no active carious lesions were recruited from a NYC hospital in 2024. Litmus paper was utilized to measure pH three times per visit: after exposure to tap water, after treatment exposure, and finally after coronal polishing. DH was tested by spraying air across each dental arch. Alternate allocation was used to assign patients to the arginine or SDF group.
Results: Thirty-six patients ranging in age from 4 to 10 (M = 6.44, SD = 1.84) were enrolled and 33 were assessed at follow-up. Follow up visits ranged from 14 to 36 days (M = 22.45, SD = 5.26). There were significant within-visit increases in oral pH relative to baseline in both groups (Ps < .001) and further increments after coronal polishing (Ps < .001). There were no significant differences in DH.
Conclusions: Partially consistent with hypotheses, findings support both SDF and arginine as effective in increasing oral pH, but not in reducing DH. Coronal polishing demonstrated additional increments, highlighting a potentially synergistic effect. These findings underscore the multifactorial etiology of caries; reduction of dental plaque may have the greatest effect on oral pH.
Identify Supporting Agency and Grant Number:

.jpg)